Results from a new study published today in the New England Journal of Medicine suggest that the Mediterranean diet works wonders for the heart.
The study, which involved 7,447 men and women already at high risk for heart disease, found that those who maintained the Mediterranean diet cut their risk of heart issues by 30 percent. The findings were so significant that researchers cut the study short after almost five years of following the participants.
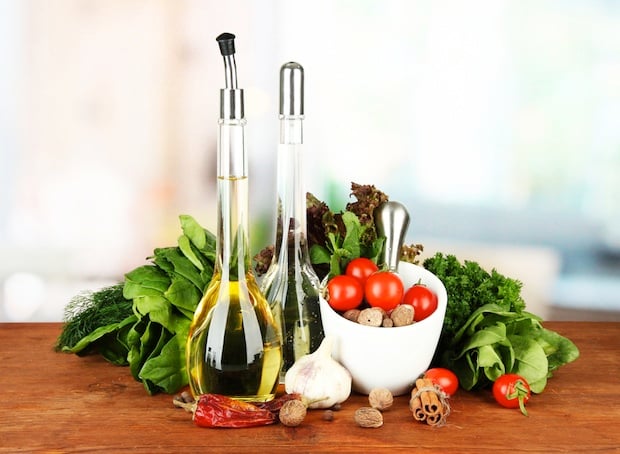
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by a high intake of olive oil, fruit, nuts, vegetables, and cereal. It also encourages a decent intake of fish and meat, and a low intake of dairy products, processed meats, and dessert. Red wine consumption is also moderate and paired with meals.
The study divided participants into three diet groups: 1) a Mediterranean diet with an emphasis on extra-virgin olive oil; 2) a Mediterranean diet with a high intake of nuts; and 3) a control diet, during which participants were only encouraged to reduce their fat intake. While all participants received nutrition and dietary advice from registered dietitians, they were not instructed on calorie intake or physical activity.
After about five years, researchers found remarkable differences between those on the Mediterranean diet and those on the control diet. First, those on the Mediterranean diet increased their intake of fish and legumes much more than the control group In particular, those on the Mediterranean diet reduced their risk of stroke, acute heart attack, and death by 30 percent. Overall, the Mediterranean diet proved to be most beneficial to reducing one’s risk of suffering from a stroke.
Researchers noted of a possible “synergy” among the nutrient-rich foods of the Mediterranean diet “that fosters favorable changes in intermediate pathways of cardiometabolic risk, such as blood lipids, insulin sensitivity, [and] inflammation.”
“Thus,” they continued, “extra-virgin olive oil and nuts were probably responsible for most of the observed benefits of the Mediterranean diets.” Olive oil contains anti-inflammatory compounds, while nuts are rich in healthy omega-3 fats.
It’s not the first time the Mediterranean diet has been touted for its heart health benefits. In 2012 it was ranked a top diet for heart health by US News & World Report, and a 2009 study found that it was the most likely diet to provide protection against coronary heart disease.
The full study is available online at the New England Journal of Medicine’s website.